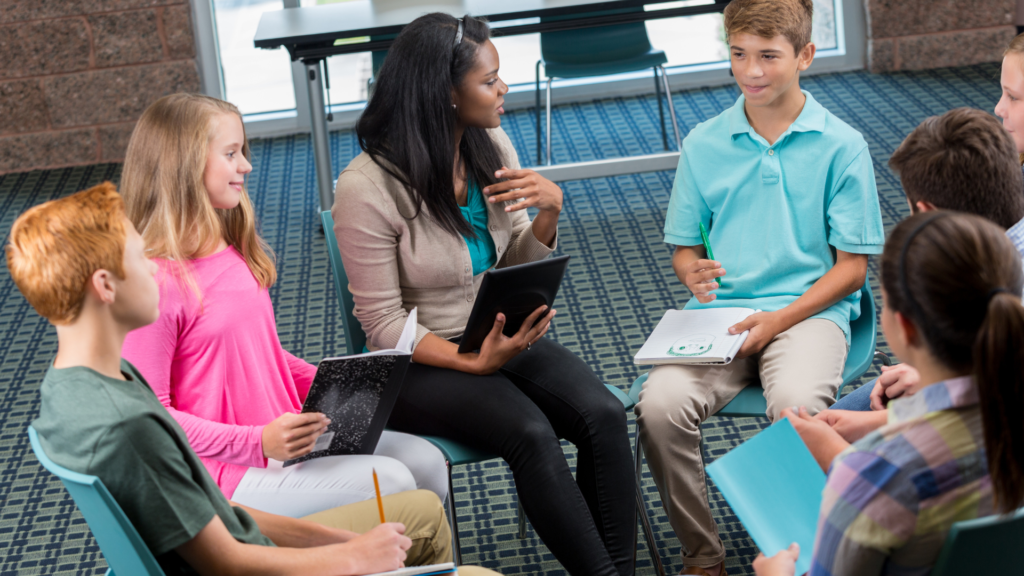
Executive function (EF) encompasses mental skills essential for planning, focusing attention, remembering instructions, and multitasking. These skills are crucial for everyday activities, influencing everything from decision-making to managing tasks. This guide will delve into the key components of executive function, how it develops, and ways to improve it, including the role of occupational therapy (OT) and speech-language therapy (SLP) in enhancing these skills.
Executive function (EF) encompasses mental skills essential for planning, focusing attention, remembering instructions, and multitasking. These skills are crucial for everyday activities, influencing everything from decision-making to managing tasks.
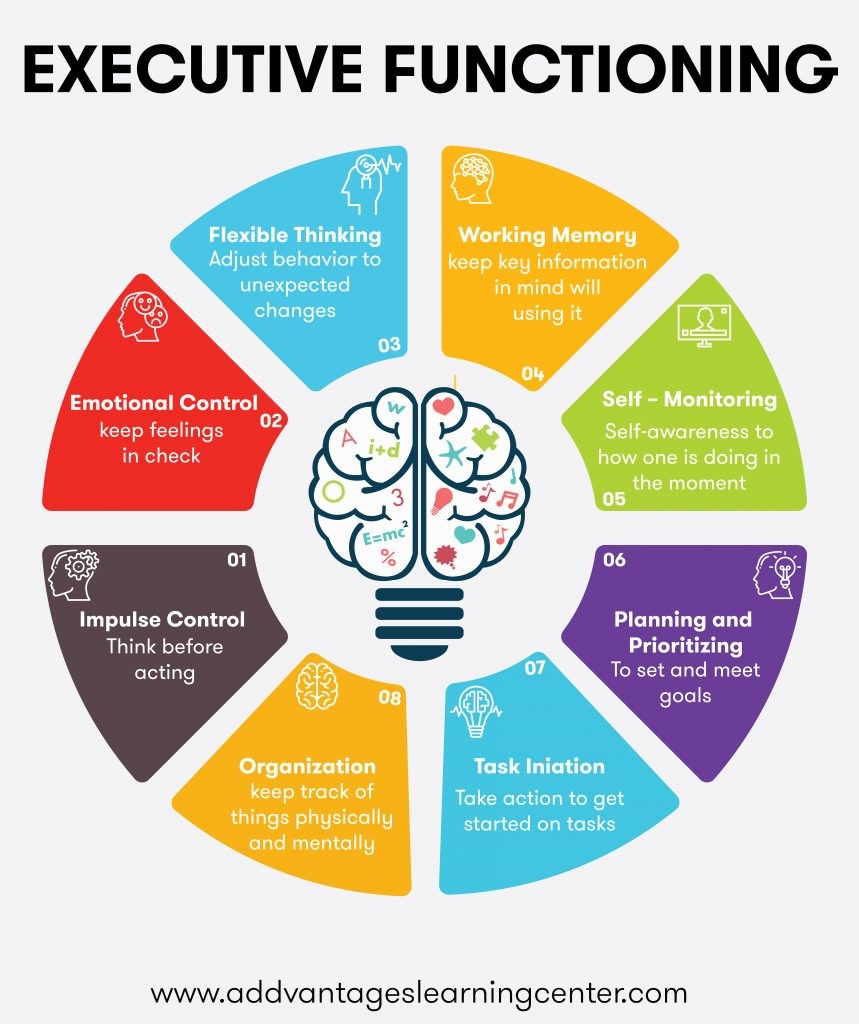
1.Working Memory:
This allows us to hold and use information for short periods. It helps us follow conversations, solve problems, and complete multi-step tasks. For example, when cooking a new recipe, working memory lets us remember the ingredients and steps without constantly checking the instructions.
2.Cognitive Flexibility:
This skill helps us switch between thinking about different concepts and adapt to new situations. It’s crucial for dealing with unexpected changes. For instance, if a meeting time changes suddenly, cognitive flexibility helps us adjust our schedule and priorities.
3.Inhibitory Control:
This is the ability to resist and control impulses and distractions, allow us to select appropriate responses, keeping us focused on our goals. It’s vital for making thoughtful decisions and avoiding negative consequences. For example, while dieting, inhibitory control helps us resist cravings for sweets.
Executive function skills develop from childhood through adulthood. Young children often struggle with planning and self-control, but these abilities typically improve with age and experience. Understanding these developmental stages can help parents and educators support children in building strong EF skills. Certain conditions, like ADHD and aging, can challenge executive function. However, strategies and therapy can help manage these challenges and improve EF.
Healthy lifestyle habits can boost executive function. Regular physical exercise, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet benefit cognitive health. Incorporating these habits into daily routines can enhance overall EF skills. Cognitive training exercises, such as puzzles and memory games, also help. Occupational therapists (OTs) and speech-language pathologists (SLPs) play a significant role in improving executive function skills.
By working together, OTs and SLPs provide comprehensive support to improve executive function skills. They create tailored intervention plans to meet individual needs.
Executive function is vital for effective decision-making and task management in our personal and professional lives. Understanding its components and importance helps us appreciate its role in daily activities. By adopting strategies to improve these skills, we can enhance our ability to achieve our goals and lead more organized, productive lives. For more insights on related topics, explore our previous post on Tips to Improve Print Awareness and Preliteracy Skills in Children.
At the Talking Brains Center in Dubai, our dedicated team of Occupational Therapists and Speech and Language Therapists is committed to helping individuals enhance their executive function and overall cognitive abilities. Discover how our specialized therapy programs can support you or your loved ones in achieving success in daily life.
